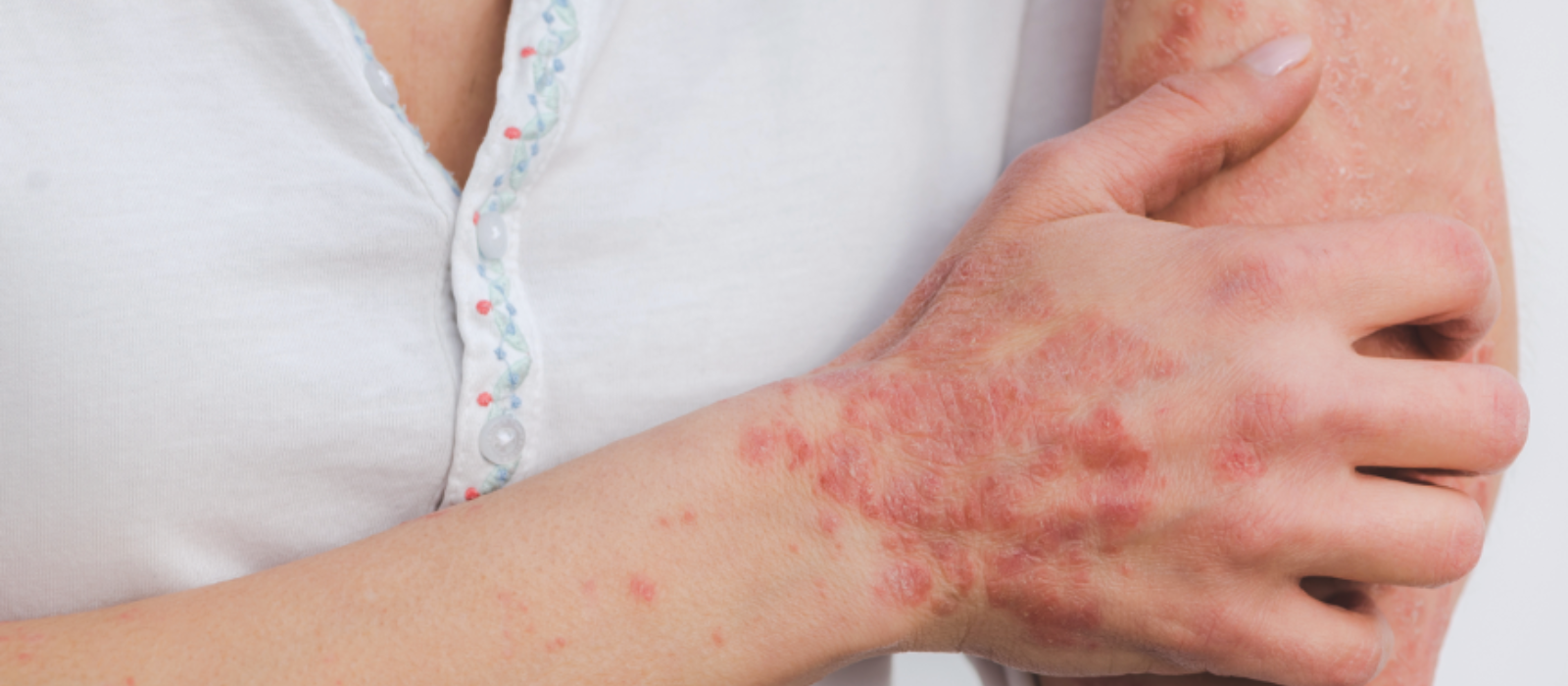
This August is Psoriasis Awareness Month. Did you know that psoriasis is an outer body manifestation of autoimmune disease?
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the skin. It is characterized by the rapid buildup of skin cells, resulting in red, flaky, and itchy patches on the skin. This condition can be physically and emotionally distressing for those who have it.
Causes of Psoriasis
The exact cause of psoriasis is still unknown, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors. People with a family history of psoriasis are more likely to develop the condition. Certain triggers, such as stress, infections, or certain medications, can also lead to flare-ups or worsen existing psoriasis symptoms.
Symptoms of Psoriasis
Psoriasis can vary in severity and presentation, but the most common symptoms include thickened, red patches of skin covered with silvery scales. These patches can appear anywhere on the body, but they are most commonly found on the scalp, elbows, knees, and lower back. In addition to the physical discomfort, psoriasis can also cause itching, burning, and pain. Some individuals may also experience nail changes, such as pitting or separation from the nail bed.
Treatment Options
While there is no cure for psoriasis, several treatment options can help manage symptoms and improve the quality of life for those affected. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the condition and the individual's response to various therapies. Some common treatments for psoriasis include:
1. Topical treatments:
Creams, ointments, and lotions containing corticosteroids, vitamin D derivatives, or coal tar can be applied directly to the affected areas to reduce inflammation and relieve itching.
2. Phototherapy:
This treatment involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet light under medical supervision. It can help slow down the excessive growth of skin cells and reduce inflammation.
3. Systemic medications:
For more severe cases of psoriasis, oral or injectable medications may be prescribed. These medications work by targeting the immune system to suppress the overactive immune response that leads to psoriasis symptoms.
4. Lifestyle modifications:
Certain lifestyle changes can also help manage psoriasis symptoms. These include maintaining a healthy weight, minimizing stress levels, avoiding triggers such as smoking and alcohol, and keeping the skin well-moisturized.
It is important for individuals with psoriasis to work closely with their healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for their specific needs.